How Telehealth is gradually becoming the frontline of patient care?
Telehealth is getting more prominent in offering streamlined patient care, and that is why the major healthcare providers are investing in the Telehealth app.

The Smartphone-led digital revolution has advanced in many fields, including healthcare, during the previous decade. The quick emergence of smartphones, as well as wearables like tablet technology and smartwatches, ushered in this revolution. Wearable sleep technology, patient electrocardiogram (ECG) tracking, and applications for detecting fall in elderly patients are all examples of these.
Combining such applications with high-speed Internet connectivity has enabled the emergence of telemedicine by effectively connecting patients and physicians via text, audio, and video in seconds.
So, what is telemedicine or telehealth! – Let’s find out
What is Telehealth?
Telehealth or Telemedicine has always been delivered through a network of specialist clinics and hospitals. Patients schedule virtual visits with the clinician who lives closest to them, and the clinician attends through the nearby clinic or hospital.

Telehealth is described as the use of electronic communications and information technology to provide clinical services to people in different locations, as well as allowing healthcare providers to push established medical treatments beyond their normal boundaries.
As an instrument for furthering the healthcare revolution, as described by the World Health Organization. Although the telemedicine trend began many years before, the onset of the COVID 19 pandemic has considerably expedited the telemedicine push, with telemedicine being used before COVID 19 inside the first two months of the pandemic. It was projected to have risen 78 times from its previous level.
The American Telemedicine Association defines Telemedicine/Telehealth as "the remote delivery of medical treatments and clinical information using telecommunications technology."
It allows for patient care while eliminating the need for physical interaction, lowering the risk of infection transmission and the strain on healthcare institutions. It can be used for long-term chronic illness management, medication adherence, doctor-patient consultations, and other remote services.
Through assistive technology like telemedicine platforms and the Internet of Things, you may use this to help a wide spectrum of individuals.
Telemedicine and digital technology have a lot of promise for increasing access and delivery in distant areas. You may also use artificial intelligence (AI) algorithms to improve pandemic defenses and response strategies.
Many medical subfields have shifted away from onsite outpatient treatment and toward remote telemedicine or e-medicine to respond swiftly to emerging requirements.
Certain persons with issues including limited trips to medical institutions, house arrest, and quarantine may benefit from telemedicine apps. Single parents, immune-compromised individuals, and patients who require assistance with transportation. Telemedicine allows for patient monitoring, home exercise, physiotherapy, psychiatric counseling, social work counseling, and remote delivery of language assistance.
The Rise of Telemedicine & Market statistics
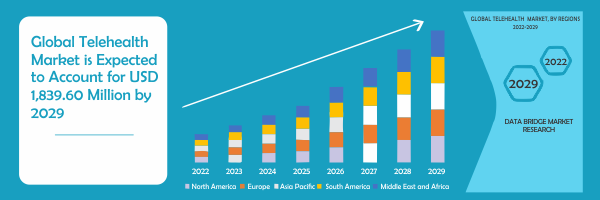
The telemedicine market in US is expected to gain market growth during the forecast period from 2022 to 2029. During the projected period of 2022 to 2029, the worldwide market for telehealth will increase at a CAGR of 7.0 percent, from the US $ 1,078.29 million in 2021 to the US $ 1,839.6 million in 2029.
Telehealth or Telemedicine use is stable at 38 times the level before the pandemic. After the initial surge to over 32% of doctor visits and outpatient visits made via telemedicine in April 2020, occupancy rates are wide and stable, ranging from 13 to 17% in all disciplines. This occupancy reflects what more than two-thirds of it reflects.
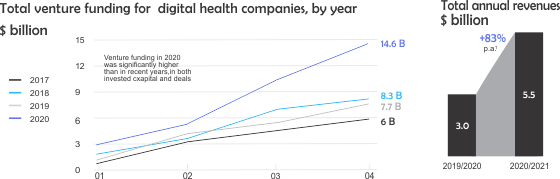
Investment in virtual care and broader digital health has soared, spurring even more innovation, with venture capitalists investing three times as much in digital health in 2020 as they did in 2017.
Investment in virtual health continues to grow. During the first half of 2021, total venture capital investment was $ 14.7 billion, surpassing all investments in 2020, which was $ 7.7 Billion – more than double. If this percentage continues, this increase reflects an annual investment of $ 25 - $ 30 billion in 2021. In addition, the total revenue of the top 60 virtual health players increased from about $ 3 billion in the previous year to $ 5.5 billion in 2020.
Similar to pre-COVID 19, customer and provider perceptions about telemedicine have improved. Awareness and usage have decreased marginally from their high in the spring of 2020. To sustain consumer and provider acceptance of virtual healthcare systems, several constraints, such as technological safety awareness, must be addressed, and models are changing to maximize hybrid virtual and face-to-face treatment.
The necessity for virtual health care services during a pandemic is highlighted in a new article published in the Journal of the American Informatics Association. During the peak of the Coronavirus pandemic, virtual emergency care visits at NYU Langone Health jumped by 683 percent, while non-emergency virtual care visits soared by 4,345 percent, according to the research.
Telemedicine reimbursement laws have also been loosened by state and municipal governments. When it comes to seeing patients from other countries or offering refunds at a lesser rate than face-to-face services, some providers are hesitant to utilize this technology.
The telehealth industry in the US is growing due to advancements in healthcare infrastructure and an increasing variety of diagnostic telemedicine platforms. However, the telemedicine market's future growth may be hampered by the lack of accessibility and high prices connected with remote monitoring devices. The telemedicine industry offers potential for expansion through partnerships and acquisitions by prominent market players.
Components, delivery modes, end consumers, and location are all used to segment the telemedicine industry. Hardware, services, and software are the three main components examined in the paper. Healthcare providers, payers, patients, and others are the primary end-users on the market.
On-premises, online, and cloud deployment modalities are also included in market research publications. Telehealth is predicted to develop rapidly in regions such as North America, Europe, Asia Pacific, and LAMEA.
When looking at the competitive landscape, it becomes clear that large IT companies are releasing big data as a service market solution and acquiring consumers in the same month. To preserve their competitive edge, major market giants are also purchasing emerging telemedicine firms or local market participants. Constant updates, collaborative ventures, and collaboration are other business methods that the two organizations prefer.
What is driving the Telehealth market in the US?
The telehealth market in US is being shaped by several drivers, constraints, and opportunities.

Increasing advancements in telecommunications:
Telehealth is quickly expanding in the healthcare industry, enabling improved access to treatment for those who are underserved as well as flexibility and convenience for both patients and clinicians.
With the rise of telemedicine, several digital medical codes routinely used by Medicare and private payers are being used. Costs have decreased as telecommunications technology progresses, and telemedicine has expanded substantially over the previous decade.
Increased prevalence of chronic and chronic diseases:
Due to the COVID19 pandemic, the chronic condition of many patients is not well controlled and only 50% of patients with a chronic condition are taking the drug as prescribed, so many healthcare providers are calling or there is a need for a rapid transition to telemedicine software, including video visits.
Lack of doctors:
The growing shortage of doctors has led to increased patient reliance on emergency clinics, emergency rooms, and retail clinics, often increasing treatment costs. Patients no longer benefit from having a doctor. Instead, when you go from one institution to the next, you will need to meet several care providers.
Telehealth software systems ease the strain by lowering healthcare expenses, eliminating administrative hurdles, and allowing clinicians to visit more patients throughout the day.
How the stakeholders can benefit from Telehealth?
In 2022, North America is dominating due to the presence of big market players along with the largest consumer market with high GDP, due to the rise of digital healthcare platforms and the launch of technologically advanced treatment support systems. Because of the development of virtual healthcare delivery platforms for accurate diagnoses and patient therapy management, the United States telehealth market is predicted to expand.
North America now dominates the worldwide telehealth market in terms of market share and revenue, and this dominance will continue during the projected period. The North American region is expected to show the highest growth due to the rise in virtual healthcare delivery platforms for accurate diagnostics and patient therapy management.
This is owing to the existence of huge market participants as well as the world's largest consumer market with a high GDP, as well as the emergence of digital healthcare platforms and the introduction of technologically enhanced treatment support systems. Market growth would be aided by increasing the number of domestic market participants and their establishments.
The ongoing COVID 19 epidemic is forcing providers and consumers to swiftly adapt to telemedicine. In many hospitals, telehealth visits have climbed by more than 300 percent, and others have now surpassed conventional telemedicine visits by 10,000 percent. With the effectiveness of pandemic telehealth, this short-term solution is likely to become a long-term one, allowing hospitals to deliver remote patient care more regularly in the future.
Of course, the rise in virtual care is a direct result of the crisis, since patient care groups were obliged to stop providing non-essential face-to-face services last spring. Once a result, expecting telehealth contacts to stay at such high levels is impractical and unrealistic, especially as hospitals, healthcare systems, and healthcare organizations reopen.
At the same time, many argue that the "telehealth trial," which began in April of last year, won the court of public opinion, resulting in more patients and physicians embracing the technology and, eventually, sustainable expansion across the business. The facts, however, indicate that this was not the case. The amount of telehealth interactions that make up a provider's weekly baseline visits has already dropped from its peak in April, according to a Commonwealth Fund study dated June 2020.
Why is Telehealth the future of patient care?
More occupational therapists are seeing the value of incorporating telehealth into their usual face-to-face services. Setting up the correct system and mastering the basics might be challenging, but serving telepractice customers offers a lot of flexibility for OTs and patients, as well as a terrific method to increase your client base.

With the growth of COVID, this sort of flexibility has become increasingly crucial to maintain service consistency and accomplish patient outcomes.
Increase parent / caregiver involvement:
When children attend a home-based therapy session, their parents or guardians have a unique chance to become facilitators. This enables you to provide more practical assistance for your child's learning and development than would otherwise be feasible.
You may also need to contact your caregiver ahead of time to manage technical aspects like logins and passwords so that treatment time may be spent on therapy rather than technological problems.
This is especially true if the patient is unable to do so alone and does not always have access to a facilitator.
You may also set expectations with your parents or guardians so that everyone knows exactly what to anticipate from the session, especially because parents may be engaged in some cases.
Better learning environment:
Some therapists are hesitant to implement remote treatment into their usual practices because they are unsure how their clients will react, yet many youngsters are delighted with the technology. This is a fun and interesting method to keep them engaged during their downtime.
Telehealth is a suitable atmosphere for certain customers since they may engage with them from the comfort of their own homes.
Easy to get started:
It may seem intimidating to begin integrating telehealth into your practice, but all you need is:
- Computer
- A wide-angle camera may be necessary to deliver classroom services via a smartboard headset with a microphone, which is most commonly integrated into mobile technology.
- Access to high-speed broadband internet
- A confidential location where you may safeguard your privacy
- HIPAA-compliant software
We should expect big changes in the national healthcare system as more providers utilize telehealth. These providers are less likely to revert to the status quo if they use telehealth.
Patients may arrange appointments online, refill medicines, and speak with a skilled healthcare expert without ever leaving their house. More people may seek similar treatments in the following months and years as the virus persists in diverse regions. Patients may seek treatment closer to home rather than going to an emergency department. The flexibility of telehealthcare also allows patients to be more choice in their medical care.
The stakeholders must optimize their provider network, accelerate value-based contracts and give incentives to telehealth. Define redemption and target service approaches (beyond immediate COVID 19 countermeasures), incorporate them into contract design, optimize network and value-based models, and include virtual health. Align the incentive to use telehealth, especially for chronic patients, with the shift to a risk-based payment model.
Healthcare providers must integrate virtual health into their treatment plan. Payers are reconsidering their involvement in providing care, from asset ownership to value-based contracts and everything in between because it creates an enormous disruption to providers.
How to implement Telehealth into your medical practice?
To implement Telehealth into the practice, the providers need to include the following:
- As an alternative to low-acute emergency department (ED) visits, on-demand virtual emergency medical treatment should be made available. The most popular telemedicine use cases among payers today are these care requirements. This enables users to speak with a stranger provider over the internet to solve immediate issues (such as severe sinusitis) and avoid going to emergency rooms or centers if required. This type of application may be expanded to cover the majority of low vision visits previously seen in the ED.
- Primary care, behavioral medicine, and certain specialist therapies are among the services that should be available during virtual patient visits. To increase patient convenience, access, and continuity of treatment, an omnichannel care model that takes full use of virtual visits combines telemedicine and face-to-face care with a consistent set of providers.
- Nearly virtual office visits extend the ability of patients to conveniently access care outside the provider's office by providing virtual access to doctors' visits at near-home testing and vaccination sites.
- Virtual domestic fitness offerings leverage digital visits, allowing a number of those offerings to be introduced remotely, which include a part of an evaluation, affected person and caregiver education, bodily therapy, occupational therapy, and speech therapy. Direct offerings, which include wound care and help with day-by-day residing routines, might nevertheless arise in a person, however digital domestic fitness offerings ought to decorate the affected person`s and caregiver`s experience, amplify the attain of the caregivers, and enhance connectivity with the wider care team.
- The assisted home medicine delivery must be there. It can be accomplished by utilizing remote monitoring to enhance patient management and symptom monitoring, giving self-service tools for patient education, and providing staff with a telehealth app.
Why do you need Percipience Solutions?
If you are concerned about the sustainability of your facility, consider optimizing your telehealth program. Keep an eye on the latest trends in telehealth and find ways to update your existing technology. In addition to smart tablets, electronic health records, and predictive analytics, providers use telemedicine technology to work with professionals in real-time to improve the quality of care.
Percipience solutions offer end-to-end software development that creates a patient-centric care approach to enable patients to enjoy all the comfort of virtual care.
We can help you to make reservations online, update your personal information, and view medical records. With our custom Telehealth app, you can simplify the patient experience to stay competitive in a changing industry.
We will make sure your telemedicine program is easy to use for both patients and staff. Eliminate redundant processes and complex interfaces that can delay supply. This will increase efficiency and allow more patients to be treated in less time.
