Blockchain Technology in Healthcare: Covering and Reviving the Loopholes
Since its inception in the last decade, the integration of Blockchain in healthcare is changing our idea of patient care and patient-centric data management.

Blockchain technology has grown in popularity over the last decade, attracting attention from a variety of industries including banking, government, energy, and health.
Here in this blog, we aim to provide a comprehensive overview of the relationship between blockchain and healthcare.
The introduction of new technologies such as the Internet of Things and big data has aided in the growth and innovation of healthcare throughout the world, as well as the creation of a smart healthcare system.
Smart healthcare is a medical system that uses the Internet of Things, data transmission, and exchange technologies to construct medical and health services and optimize management, using medical cloud data at its center. The smart healthcare business is now making significant development, but there are still issues with data and system security.
Decentralization, anonymity, tamper resistance, and auditability are all properties of blockchain, which is the essential technology of the fourth industrial revolution.
The combination of blockchain in healthcare today mitigates the weaknesses of traditional smart healthcare in information sharing, data security, and privacy, optimizes user-centric smart healthcare systems, and involves governments, businesses, and individuals to be smart. You can build a multi-party medical alliance chain that realizes.
As a result, we've found various state-of-the-art use cases for blockchain technology, such as exchanging electronic medical data, remote patient monitoring, medicine supply chain, and so on.
But before that, let us tell you what is Blockchain in healthcare –
Introducing Blockchain Technology in Healthcare
To understand Blockchain healthcare, we need to know the key concepts of Blockchain first. Blockchain has emerged as one of the most promising technologies in the recent decade, attracting the attention of various academic studies and industries.
Satoshi Nakamoto first proposed this notion in a white paper published in 2008. It's a decentralized, distributed, immutable ledger that's used to securely record transactions across multiple computers in a peer-to-peer network without the involvement of a third party.
A blockchain is a public ledger made up of a collection of blocks that maintains track of all transactions on your network. The block is made up of two parts: a head and a body. Each block's header includes the hash of the preceding block. As a consequence, the blocks form a chain or linked list, with each block structure building on top of the preceding one.
The timestamp indicates when the block was released, zero, which is an arbitrary number that miners change frequently to get a specific hash value to solve a math puzzle, and a Merkle tree basically does the Reduced effort required to verify transactions inside the block is also included in the block header.
A Blockchain transaction is a small unit of work that is recorded in public blocks. Each transaction is confirmed by the majority of system users. Once transactions are included in the blockchain, inviolability is guaranteed. Regarding the immutability of the blockchain, each participant copies, stores, and maintains a unique copy of the ledger.
Business logic is written using smart contracts. Smart contracts are self-executing code on the blockchain framework that can be processed directly regardless of the type of blockchain. Smart contracts become permanently tamper-proof when integrated with the blockchain because no one can change what is encrypted, self-verifies through automated capabilities, and self-executes once the rules are established.
Blockchain Technology uses in Healthcare
Healthcare is one of the promising industries for blockchain. In 2016, the Office of the National Healthcare Information Technology Coordinator (ONC) recognized the relevance and value of the technology and published a white paper idea contest on the potential use of blockchain in medicine. Due to this difficulty, several blockchain-based health applications have been presented.
In this part, we'll look at key findings organized by use case, including electronic medical records, remote patient monitoring, drug supply chains, and health insurance claims.
Electronic Medical Records (EMRs):
To revolutionize healthcare, the focus should be on health data management, which might benefit from the ability to integrate heterogeneous systems and enhance the accuracy of Electronic Health Records (EHRs).
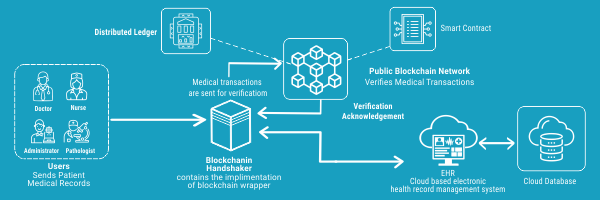
While the words electronic medical records (EMRs) and electronic health records (EHRs) are sometimes used interchangeably, there is a distinction between the two. The phrase "electronic medical records" (EMR) was coined initially, and it refers to a digital version of a clinician's paper documents.
EMR keeps a patient's medical history and treatment history in a single visit. EHRs, on the other hand, focus on the patient's overall health and provide a broader perspective on patient care beyond the usual clinical data collected in the clinic.
Electronic medical data are a part of medical data management. To get up-to-date affected person's history, digital medical records offer an on-hand fitness file in a digital and encrypted format, that's distinctly touchy data that desires to be shared amongst peers.
Patients` diagnostic and remedy facts are nevertheless dispersed in separate sanatorium systems, and contemporary digital scientific facts can not guarantee the security, privacy, or availability of sensitive facts.
As a result, patients may lose ownership of available health data while the institution maintains primary control. Distributing electronic medical records using blockchain technology is customer-centric and patients retain ownership of their records.
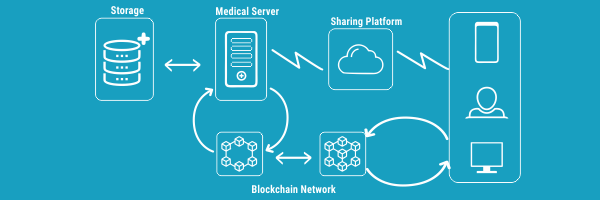
The blockchain's decentralized, self-trusted, and tamper-resistant structure assures the safe storage and distribution of medical data while also drastically reducing the time it takes to share data and total expenses. Patients will also focus more on their healthcare since they may engage in their health records.
Interoperability and data sharing:
Ineffective interoperability causes two types of problems:
- Patient identification problems
- Information blocking
This happens when the healthcare provider excessively restricts the transmission of patient data or electronic medical information. The lack of globally recognized patient identity and information block practices is a significant barrier to effective medical delivery.
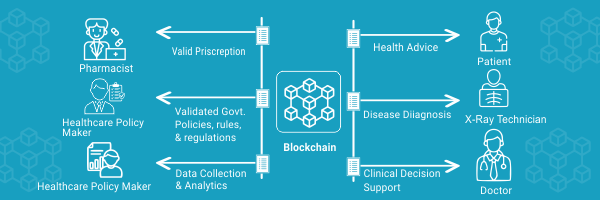
Blockchain healthcare Interoperability is also important, especially in epidemics like the corona pandemic. The timing of the outbreak is an urgent need for a broader data-sharing infrastructure that helps simplify communication between patients and healthcare providers and facilitate the flow of information needed to address public health concerns. When patients meet a doctor who is not their GP, they need easy access to their medical records.
The improved health data flow would also allow clinicians to do remote monitoring and telemedicine consultations. This gives people the ability to keep their doctors up to date on their medical history. As the number of instances of the coronavirus rises, timely and transparent information, such as how individuals may estimate their risk, present symptoms, and react to therapy, becomes increasingly important. Public health emergencies emphasize the present system's lack of interoperability even more.
Blockchain technology has the potential to considerably simplify the process of exchanging healthcare data and aid in the resolution of the healthcare industry's interoperability challenge.
Patients are identifiable in the healthcare blockchain by their hash ID, which will be their unique identity. The hashing ensures that the ID is unique and that the user's privacy is protected. Patients would be in charge of disclosing the decryption key for their related data blocks to their preferred healthcare practitioner. It improves security, privacy, and interoperability, and it has the potential to place patients at the heart of the ecosystem.
Accurate, up-to-date, and thorough medical records would be extremely beneficial to both patients and physicians.
Remote Patient Monitoring:
When we have a health problem, we frequently go to a primary care clinic to see a doctor. This is referred to as episodic care. A comprehensive approach, on the other hand, aims to avoid problems and improve people's quality of life. This move from medical clinics can be aided by remote healthcare.
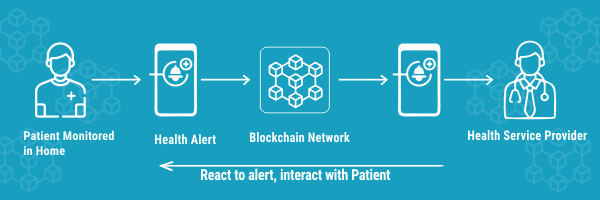
The majority of us now own smart gadgets such as smartphones and wearables. Many of our health markers may be measured using these. You save time, and the medical experts save time as well.
However, our traditional healthcare systems emphasize episodic care, but RPM seeks to emphasize preventative care as well. Consider Electronic Health Records (EHRs). They are built to facilitate episodic care by their very nature. Incorporating RPM data into EHRs has legal implications as well. Stakeholders in the healthcare business must first determine their strategy before transforming existing systems to enable RPM.
We currently have wearable gadgets for a variety of healthcare-related applications, but they are not sufficiently useful for continuous usage. For RPM to deliver value, it must be used continuously for a lengthy period.
Blockchain for healthcare can aid in assuring the accuracy of data captured by RMP devices as well as allowing safe and rapid data sharing. To comprehend how, we must first comprehend how blockchain operates, which is as follows:
- Blockchain is a distributed and decentralized network. Computers on this network are called "nodes" and anyone can join the public blockchain network.
- Every node has the same level of authority and has access to the whole blockchain's transaction history. As a result, each node becomes a full ledger of all transactions.
- Because the network will be maintained by the other nodes, no hacker can destroy the network by compromising one machine.
- Data is protected from manipulation through digital signatures, contemporary cryptographic hash functions, and strict consensus procedures.
Medical Data Security:
Recent security breaches in healthcare information have heightened concerns about data security and patient privacy. In 2017, 45 percent of ransomware attacks targeted healthcare businesses, according to Beazley, a worldwide cybersecurity insurance provider.
The amount of medical data breaches and compromised healthcare information is on the rise. The number of documented breaches in the healthcare business increased from around 20 in 2009 to more than 350 in 2017, according to the HIPPA Journal.
The variety of breaches within the healthcare commercial enterprise resulted withinside the disclosure of thirteen million general healthcare statistics in 2018, in keeping with the Department of Health and Human Services. In 2016, there was at least one health data breach each day, compromising more than 27 million patient records. In 2018, hackers gained access to 1.4 million patients' medical information from the UnityPoint Health hospital network. This was the year's greatest medical data leak in the United States.
Many healthcare institutions keep sensitive health data in a central place, which is vulnerable to ransomware and other intrusions due to an aged legacy IT architecture. Because of the volume of data maintained by healthcare providers, they are frequently targets of sophisticated cyber-attacks.
Access to patient data and other vital information may be debilitating for any provider, costing victims millions of dollars. To anticipate risks before they become serious, healthcare businesses are investing in sophisticated security technologies such as enhanced data backups, advanced data encryption, AI, and real-time security platforms.
Data security and patient privacy concerns, as well as an increase in the number of cyberattacks, have generated a compelling demand for improved IT security. To anticipate risks before they become serious, healthcare businesses are investing in sophisticated security technologies such as enhanced data backups, advanced data encryption, AI, and real-time security platforms.
For healthcare data security and identity management, blockchain has several advantages. It can prevent attacks and keep personal information out of the wrong hands. When data is uploaded to the blockchain, it is encrypted, making it unchangeable and hard to decrypt. It authorizes transactions using a private identity key that is only known by the user.
In contrast to current healthcare data technologies, a healthcare professional would only be able to view a patient's medical data if they had specific access to the blockchain record. Better data collaboration among clinicians enhances the chances of a correct diagnosis and successful treatment, as well as allows healthcare institutions to provide cost-effective care.
Patients' information may be kept safe and private while still allowing them to share it with any service providers they want. It ensures the legitimacy of anti-counterfeiting procedures by confirming ownership of medical information.
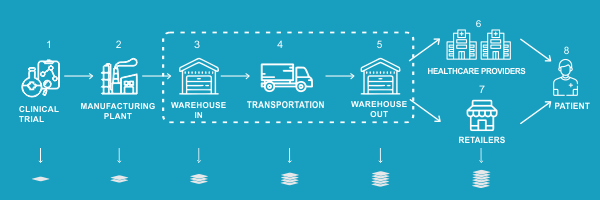
Pharmaceutical supply chain:
Another use of blockchain technology in healthcare that has been found is in the pharmaceutical business. Patients may suffer serious effects if they get counterfeit or insufficient drugs. Blockchain technology has been recognized as a potential solution to this issue.
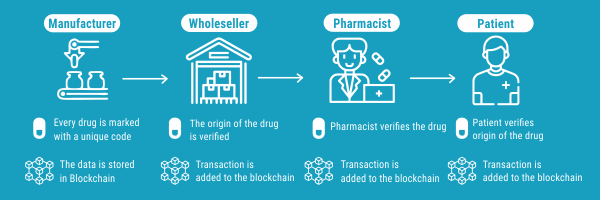
Anticounterfeiting costs pharmaceutical businesses almost USD 200 billion every year. By offering visibility, security, and medicine tracking, blockchain can help to tackle the problem of counterfeit drugs.
To combat the counterfeit problem, the system employs elements like proof of authenticity and point-by-point monitoring capabilities, assuring that once a medicine is manufactured, it is real.
Before purchasing the medications, the consumer may check their legitimacy. Not only may blockchain in healthcare be used to trace pharmaceuticals from manufacture through distribution to patients, but it can also be used to record a drug's effect on a patient in a database after use for future statistics.
Pharmaceutical companies are utilizing blockchain to follow the travel of raw materials, compounds, and components from the source to the patient at every stage of the supply chain.
Blockchain healthcare can potentially be used by pharmaceutical research communities to secure medical and health-related supply chain data. The capacity to identify the origin and validity of medical items is thought to be improved by blockchain, which increases supply chain security.
As controlled substance usage becomes increasingly frequent, blockchain allows for the detection of the whole range of issues associated with pharmacological therapy.
Market Statistics for Blockchain in Healthcare
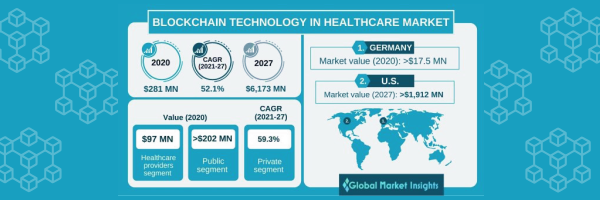
Blockchain Technology in Healthcare Market is expected to grow at a 52.1 percent CAGR from 2021 to 2027, with market size of USD 281 million in 2020.
Blockchain technology is expected to grow in popularity as the Internet of Things (IoT) becomes more widely used in healthcare. The adoption of new and novel computer technology, such as blockchain, enhances the healthcare sector's current skills. The Internet of Things (IoT) is supporting doctors and medical practitioners in the early detection of a variety of diseases.
Clinical trials accounted for 18 percent of the blockchain technology in the healthcare market share in 2020, owing to the wide range of applications for enhancing clinical trial quality.
Implementing this blockchain technology in healthcare improves recruiting, allows for full decentralization, supports governance with real-time decision-making, and optimizes the performance of repetitive activities, all of which help trials run smoothly.
For the whole document flow of a clinical study, blockchain technology assists in achieving a significant level of historicity and inviolability of data. This also enables safe clinical trial automation using smart contracts, ensuring traceability and preventing a posteriori rebuilding.
Because of the wide range of uses and applications of blockchain technology in healthcare, the healthcare providers market is expected to generate USD 97 million in 2020. Healthcare providers benefit from digital ledger technology because it streamlines the drug supply chain and allows for the safe transmission of patient medical information.
In 2020, the United States dominated the North American blockchain technology in the healthcare industry, which is expected to reach USD 1.91 billion by 2027. The recent breakthroughs in blockchain technology, as well as many government efforts encouraging the use of these novel platforms in healthcare, account for the majority of the market share.
To know more about Blockchain technology in healthcare, follow us on our Instagram @percipiencesolutions and Facebook @PercipienceSolutions channels, or get in touch with us at https://percipiencesolutions.com/contact
